상세 컨텐츠
본문
모든 리액트 컴포넌트는 라이프사이클(수명 주기)이 존재합니다. 컴포넌트의 수명은 페이지에 렌더링 되기 전, 준비 과정에서 시작하여 페이지가 사라질 때 끝납니다.
컴포넌트의 라이프사이클 메서드를 사용하는 경우는 다음과 같습니다.
- 컴포넌트를 처음으로 렌더링할 때 어떤 작업을 처리해야 하는 경우
- 컴포넌트를 업데이트하기 전후로 어떤 작업을 처리해야 하는 경우
- 불필요한 업데이트를 방지해야하는 경우
라이프사이클 메서드는 클래스형 컴포넌트에서만 사용 가능합니다. 함수 컴포넌트에서는 Hooks 기능을 사용하여 비슷한 작업을 처리할 수 있습니다.
I. 라이프사이클 메서드의 이해
라이프사이클 메서드의 종류는 총 9가지입니다.
- Will 접두사가 붙은 메서드 : 어떤 작업을 작동하기 전에 실행되는 메서드
- Did 접두사가 붙은 메서드 : 어떤 작업을 작동한 후에 실행되는 메서드
- 위의 메서드들은 컴포넌트 클래스에서 덮어써 선언함으로 사용 가능
라이프사이클은 총 3가지 카테고리로 나뉩니다.

마운트, 업데이트, 언마운트 카테고리를 간단히 알아보고 큰 흐름을 먼저 이해해봅시다.
1. 마운트
DOM이 생성되고 웹 브라우저상에 나타나는 것을 마운트(mount)라고 합니다.
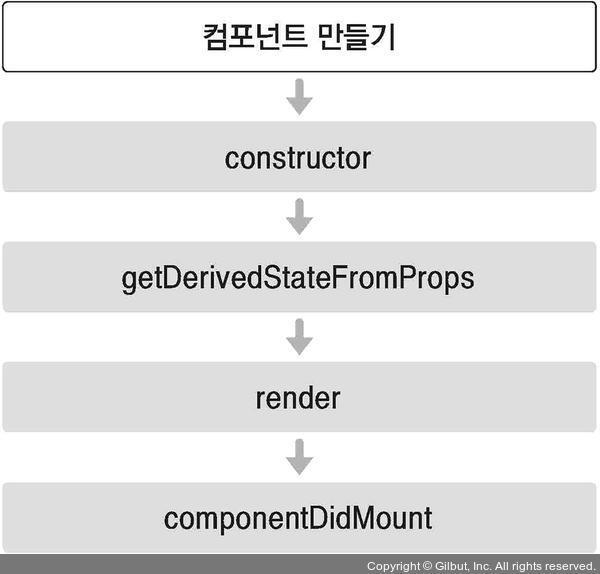
- constructor : 클래스 생성자 메서드, 컴포넌트를 새로 만들 때마다 호출됨
- getDerivedStateFromProps : props에 있는 값을 state에 넣을 때 사용하는 메서드
- render : 준비한 UI를 렌더링하는 메서드
- componentDidMount : 컴포넌트가 웹 브라우저상에 나타난 후 호출하는 메서드
2. 업데이트
컴포넌트는 다음과 같은 4가지 경우에 업데이트를 진행하게 됩니다.
- props가 바뀔 때
- state가 바뀔 때
- 부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링될 때
- this.forceUpdate로 강제로 렌더링을 트리거할 때
컴포넌트가 업데이트되면 다음 메서드를 호출하는 과정을 거칩니다.

- 컴포넌트는 다양한 이유로 업데이트됨
1) 부모 컴포넌트에서 넘겨주는 props 값이 바뀌는 경우 컴포넌트 렌더링이 이루어짐
2) 컴포넌트 자신이 들고 있는 state 값이 setState를 통해 업데이트되는 경우 렌더링됨
3) 부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 되는 경우 자식 컴포넌트 또한 리렌더링됨 - getDerivedStateFromProps : 마운트 과정과 업데이트가 시작하기 전에 호출됨, props의 변화에 따라 state 값에도 변화를 주고 싶을 때 사용
- shouldComponentUpdate : true 혹은 false 값을 반환하여 컴포넌트가 리렌더링을 해야 할지 말아야 할지를 결정하는 메서드
1) true를 반환하면 다음 라이프사이클 메서드를 계속 실행
2) false를 반환하면 작업을 중지함, 즉 컴포넌트가 리렌더링되지 않음
만약 특정 함수에서 this.forceUpdate() 함수를 호출한다면 이 과정을 생략하고 바로 render 함수를 호출 - render: 컴포넌트를 리렌더링함
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate: 컴포넌트 변화를 DOM에 반영하기 바로 직전에 호출하는 메서드
- componentDidUpdate: 컴포넌트의 업데이트 작업이 끝난 후 호출하는 메서드
3. 언마운트
마운트의 반대 과정으로 컴포넌트를 DOM에서 제거하는 것을 언마운트(unmount)라고 합니다.

- componentWillUnmount : 컴포넌트가 웹 브라우저상에서 사라지기 전에 호출하는 메서드
II. 라이프사이클 메서드 살펴보기
1. render() 함수
render() { ... }- 컴포넌트 모양새를 정의하는 메서드로 컴포넌트에서 제일 중요한 메서드
- 라이프사이클 메서드 중 유일하게 필수 메서드
- this.props 값이나 this.state 값에 접근할 수 있으며 리액트 요소를 반환함
ex) div와 같은 태그, 따로 선언한 컴포넌트, null이나 false 등등 - 이벤트 설정이 아닌 곳에서 setState를 사용하거나, 브라우저의 DOM에 접근하면 안 됨
=> state 값에 변화를 주거나 DOM 정보를 가져와야 하는 경우는 componentDidMount에서 처리
2. constructor 메서드
constructor(props) { ... }- 컴포넌트의 생성자 메서드
- 컴포넌트를 만들 때 처음으로 실행됨
- 초기 state를 정할 수 있음
3. getDerivedStateFromProps 메서드
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
if(nextProps.value !== prevState.value) { // 조건에 따라 특정 값 동기화
return { value: nextProps.value };
}
return null; // state를 변경할 필요가 없다면 null을 반환
}- 리액트 v16.3 이후에 새로 만든 라이프사이클 메서드
- props로 받아온 값을 state에 동기화시키는 용도로 사용
- 컴포넌트가 마운트 될 때와 업데이트될 때 호출됨
4. componentDidMount 메서드
componentDidMount() { ... }- 컴포넌트를 만들고, 첫 렌더링을 다 마친 후 실행되는 메서드
- 다른 자바스크립트 라이브러리 또는 프레임워크 함수를 호출하거나
이벤트 등록, setTimeout, setInterval, 네트워크 요청 같은 비동기 작업 처리를 함
5. shouldComponentUpdate 메서드
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) { ... }- props 또는 state를 변경했을 때 리렌더링을 시작할지 여부를 결정하는 메서드
- true 혹은 false 와 같은 불리언 값을 반환함
- 컴포넌트 정의 시 이 메서드를 따로 생성하지 않으면 언제나 true 값을 반환
- 이 메서드에서 false 값이 반환되면 업데이트 과정은 중지됨
- 현재 props와 state는 this.props와 this.state로 접근
새로 설정될 pros와 state는 nextProps와 nextState로 접근함 - 컴포넌트를 최적화하고자 리렌더링 방지할 때 false 값을 반환하게 만듦
6. getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 메서드
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if(prevState.array !== this.state.array) {
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight } = this.list
return { scrollTop, scrollHeight };
}
}- 리액트 v16.3 이후에 새로 만든 라이프사이클 메서드
- render 에서 만들어진 결과물이 브라우저에 실제로 반영되기 직전에 호출하는 메서드
- 반환하는 값은 componentDidUpdate의 세 번째 파라미터(snapshot)로 전달
- 업데이트 직전의 값을 참고할 때 사용
ex) 스크롤바 위치
7. componentDidUpdate 메서드
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { ... }- 리렌더링을 완료한 후 실행되는 메서드
- 업데이트가 끝난 직후 이므로 DOM과 관련된 처리를 해도 무방함
- prevProps 또는 prevState를 사용해 컴포넌트가 이전에 가졌던 데이터에 접근할 수 있음
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate에서 반환한 값이 있다면 여기서 snapshot 값을 전달받을 수 있음
8. componentWillUnmount 메서드
componentWillUnmount() { ... }- 컴포넌트를 DOM에서 제거할 때 사용하는 메서드
- componentDidMount에서 등록한 이벤트, 타이머, 직접 생성한 DOM 등을 여기서 제거
9. componentDidCatch 메서드
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
this.setState({
error: true
});
console.log({ error, info });
}- 리액트 v16.3 이후에 새로 만든 라이프사이클 메서드
- 컴포넌트 렌더링 도중에 에러가 발생했을 때 애플리케이션이 오류 UI를 보여 줄 수 있게 해 줌
- console.log 에서 발전시켜 오류가 발생하면 서버 API를 호출하여 따로 수집하도록 할 수 도 있음
- 단, 컴포넌트 자신에게 발생하는 에러는 잡을 수 없고
자신의 this.props.children으로 전달되는 컴포넌트에서 발생하는 에러만 잡아낼 수 있음 - 이 메서드의 사용 방벙법은 포스트의 "에러 잡아내기"에서 알아보겠음
III. 라이프사이클 메서드 사용하기
배운 라이프사이클 메서드를 다음 단계별로 사용해봅시다.
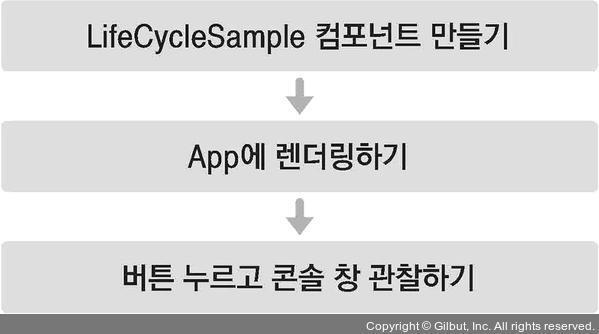
1. 예제 컴포넌트 생성
// LifeCycleSample.js
import { Component } from "react";
class LifeCycleSample extends Component {
state = {
number: 0,
color: null,
}
myRef = null; // ref를 설정할 부분
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor');
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps');
if(nextProps.color !== prevState.color) {
return { color: nextProps.color };
}
return null;
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount');
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');
// 숫자의 마지막 자리가 4면 리렌더링하지 않음
return nextState.number % 10 !== 4;
}
componentWillUnount() {
console.log('componentWillUnount');
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
number: this.state.number + 1
});
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('getSnapshotBeforeUpdate');
if(prevProps.color !== this.props.color) {
return this.myRef.style.color;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot){
console.log('componentDidUpdate', prevProps, prevState);
if(snapshot) {
console.log('업데이트되기 직전 색상: ', snapshot);
}
}
render() {
console.log('render');
const style = {
color: this.props.color
};
return (
<div>
<h1 style={style} ref={ref => this.myRef=ref}>
{this.state.number}
</h1>
<p>color: {this.state.color}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
더하기
</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default LifeCycleSample;- 메서드를 실행할 때마다 콘솔 디버거에 기록됨
- 부모 컴포넌트에서 props로 색상을 받아 버튼을 누르면 state.number 값을 1씩 더함
- getDerivedStateFromProps는 부모에게서 받은 color 값을 state에 동기화
- getSnapshotBeforeUpdate는 DOM에 변화가 일어나기 직전에 색상을 snapshot 값으로 반환
- 반환된 값은 componentDidUpdate에서 조회
- shouldComponentUpdate 메서드에서 state.number 값의 마지막 자릿수가 4이면 리렌더링을 취소
2. App 컴포넌트에서 예제 컴포넌트 사용
// App.js
import { Component } from "react";
import LifeCycleSample from "./LifeCycleSample";
function getRandomColor() {
return '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
}
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000'
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
color: getRandomColor()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>랜덤 색상</button>
<LifeCycleSample color={this.state.color}/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;- getRandomColor 함수는 state의 color 값을 랜덤 색상으로 설정
- 버튼을 렌더링하고 누를 때마다 handleClick 메서드가 호출되도록 이벤트를 설정
- 불러온 LifeCycleSample 컴포넌트에 color 값을 props로 설정
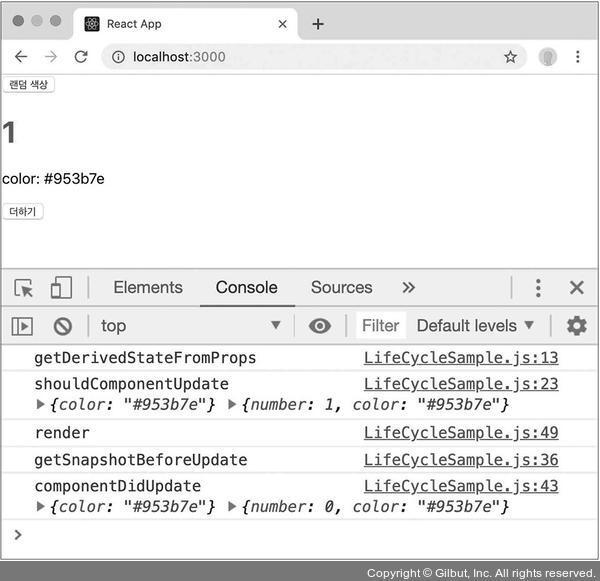
이 코드의 실행 결과는 다음과 같습니다.

라이프사이클 메서드를 실행시키면 다음과 같은 결과를 낼 수 있을 것입니다.
3. 에러 잡아내기
(1) 에러 발생시키기
LifeCycleSample 컴포넌트의 render 함수에서 에러가 발생했을 때 처리를 배워봅시다. render 함수에서 에러는 1)존재하지 않는 함수를 사용하려 하거나, 2)존재하지 않는 객체의 값을 조회하려 할 때 발생합니다.
의도적으로 render에서 존재하지 않는 props인 missing 객체 값을 조회하도록 코드를 변경해봅시다.
// LifeCycleSample.js
(...)
render() {
console.log('render');
const style = {
color: this.props.color
};
return (
<div>
{this.props.missing.value}
<h1 style={style} ref={ref => this.myRef=ref}>
{this.state.number}
</h1>
<p>color: {this.state.color}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
더하기
</button>
</div>
)
}- 다음의 코드를 저장하면 에러가 발생할 것
- 개발 서버를 실행 중이므로 어디서 에러가 발생했는지 뜰 수 있음
- 그러나 사용자가 웹 서비스를 실제로 사용할 때는 흰 화면만 뜰 것임
- 에러가 발생했다는 것을 사용자가 인지하도록 부가적인 처리가 필요함
(2) 에러 처리 컴포넌트 작성
에러를 잡아주는 ErrorBoundary 컴포넌트를 작성해봅시다.
// ErrorBoundary.js
import { Component } from "react";
class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
state = {
error: false
};
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
this.setState({
error: true
});
console.log({ error, info });
}
render() {
if( this.state.error ) return <div>에러가 발생했습니다.</div>
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;- 에러가 발생하면 componentDidCatch 메서드가 호출
- 메서드는 this.state.error 값을 true로 업데이트
- render 함수는 this.state.error 값이 true 라면 에러가 발생했음을 알리는 문구 보여줌
(3) App 컴포넌트 재작성
App.js에서는 LifeCycleSample 컴포넌트를 감싸줍니다.
// App.js
import { Component } from "react";
import LifeCycleSample from "./LifeCycleSample";
import ErrorBoundary from "./ErrorBoundary"
function getRandomColor() {
return '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
}
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000'
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
color: getRandomColor()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>랜덤 색상</button>
<ErrorBoundary>
<LifeCycleSample color = {this.state.color} />
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
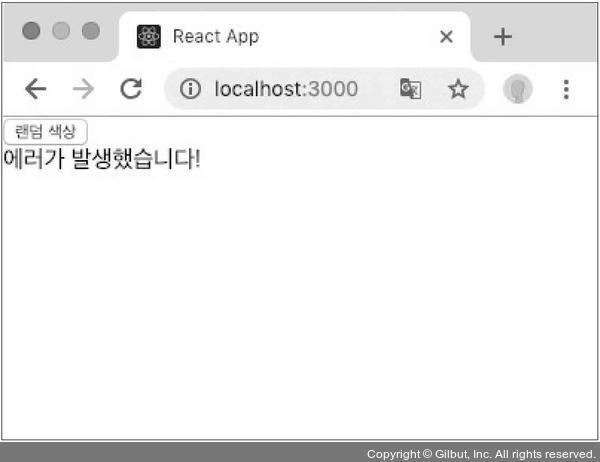
코드를 작성하고 저장하면 다음과 같은 문구를 확인할 수 있습니다.
IV. 정리
컴포넌트의 라이프사이클 메서드 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
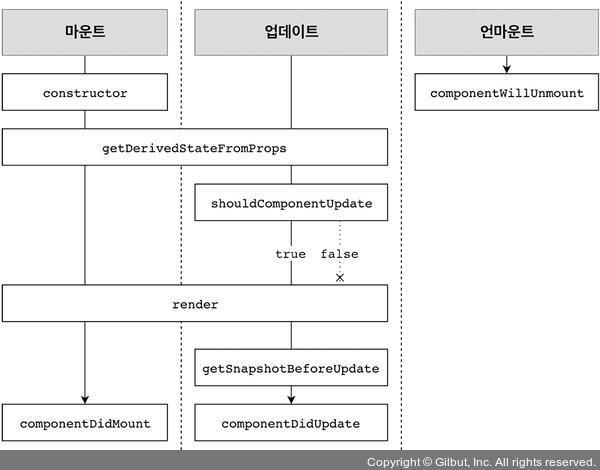
- 라이프사이클 메서드는 컴포넌트 상태에 변화가 있을 때마다 실행 되는 메서드
- 이 메서드들은 서드파티 라이브러리를 사용하거나, DOM을 직접 건드려야 하는 상황에서도 유용
- 컴포넌트 업데이트 성능을 개선할 때는 shouldComponentUpdate가 중요하게 사용됨
📌 Quiz
- 모든 리액트 컴포넌트는 컴포넌트를 처음 렌더링할 때, 업데이트하기 전후, 불필요한 업데이트를 방지해야하는 경우 ( ) 메서드를 사용합니다.
- ( ) 접두사가 붙은 메서드는 어떤 작업을 작동하기 전에 실행되는 메서드이고 () 접두사가 붙은 메서드는 어떤 작업을 작동한 후에 실행되는 메서드
- DOM이 생성되고 웹 브라우저상에 나타나는 것을 ( ) 라고 합니다.
- 컴포넌트는 props나 state가 바뀔 때 부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 될 때 ( ) 됩니다.
- 라이프사이클 메서드 중 유일하게 필수 메서드이자 컴포넌트 모양새를 정의하는 메서드로 컴포넌트에서 제일 중요한 메서드는 ( ) 메서드입니다.
- shouldComponentUpdate 이 반환하는 값이 ( )라면 컴포넌트가 리렌더링되지 않습니다.
- ( )는 컴포넌트를 DOM에서 제거할 때 사용하는 메서드입니다.
- state의 색을 렌덤으로 바꾸는 메서드(getRandomColor) 를 작성해보세요
- LifeCycleSample 에서 발생한 에러를 처리하는 ErrorBoundary 컴포넌트를 작성했다고 생각해봅시다. 에러 발생시 ErrorBoundary가, 정상 처리시 LifeCycleSample 가 작동되도록 다음의 App.js를 수정하시오.
// App.js
import { Component } from "react";
import LifeCycleSample from "./LifeCycleSample";
function getRandomColor() {
return '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
}
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000'
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
color: getRandomColor()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>랜덤 색상</button>
<LifeCycleSample color={this.state.color}/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
- 라이프사이클
- Will / Did
- 마운트
- 업데이트
- render
- false
- componentWillUnmount
function getRandomColor() {
return '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
}
9.
// App.js
import { Component } from "react";
import LifeCycleSample from "./LifeCycleSample";
import ErrorBoundary from "./ErrorBoundary" //수정
function getRandomColor() {
return '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
}
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000'
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
color: getRandomColor()
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>랜덤 색상</button>
<ErrorBoundary> //수정
<LifeCycleSample color = {this.state.color} />
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;◎ 다라
'22-23 > 22-23 리액트 스타터 2' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [리액트스타터2] 9장. 컴포넌트 스타일링 (0) | 2022.12.01 |
|---|---|
| [리액트스타터2] 8장. Hooks (0) | 2022.11.24 |
| [리액트스타터2] 6장. 컴포넌트 반복 (0) | 2022.11.10 |
| [리액트스타터2] 5장. ref (1) | 2022.11.05 |
| [리액트스타터2] 4장. 이벤트 핸들링 (0) | 2022.10.13 |